When building Multimodal AI (Text + Vision) workflows with Mistral, standard low-code abstractions often fail to capture the complexity of the data payload. Standard Mistral models (mistral-large, mistral-medium) are text-only. To analyze images, you must use Pixtral (pixtral-12b).

This guide documents the rigorous engineering approach to building a meal analysis app using Mistral Pixtral via direct API integration.
The Engineering Challenge
n8n provides a pre-built "Mistral Chat Model" node. However, this node is primarily optimized for text generation and may lack the specific binary file handling required to pass an image into the context window of Pixtral effectively.
To ensure reliability, we drop down a layer of abstraction. Instead of using the pre-built node, we construct raw HTTP Requests to the Mistral API, allowing for precise control over the binary encoding and payload structure.
The Architecture
We are building a pipeline that receives an image, converts it into a format the LLM can "read" (Base64), and strictly enforces a JSON output.
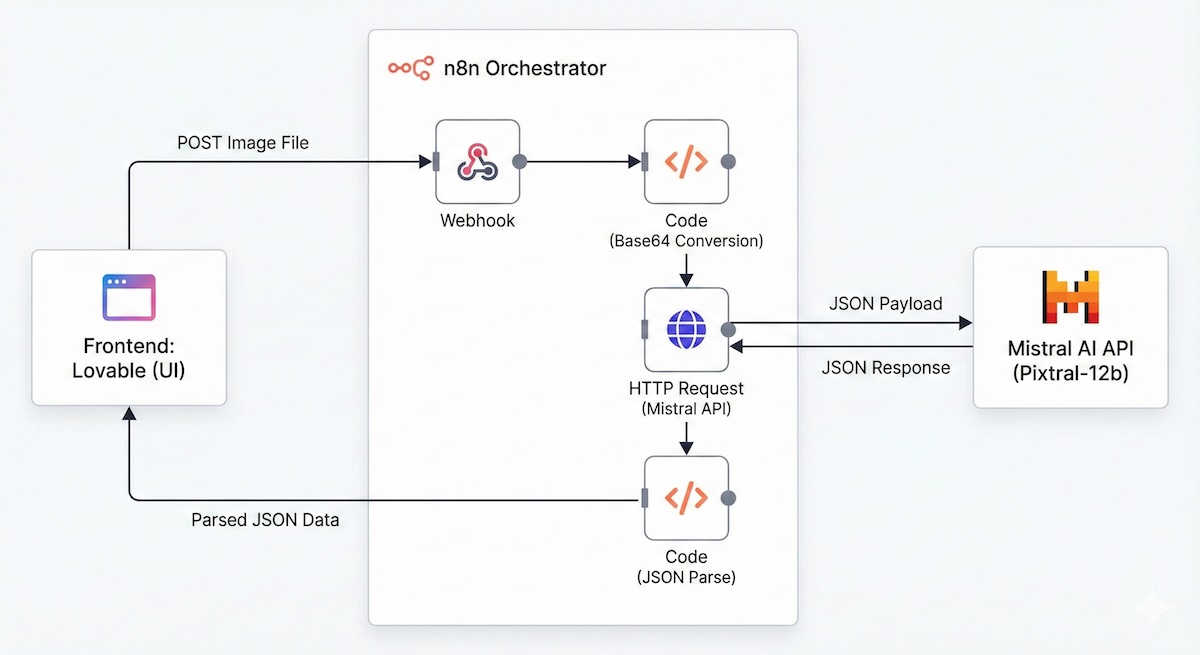
The entry point remains standard. We accept a POST request containing the image file.
Method: POST
Path: meal-ai
Response Mode: Respond When Last Node Finishes (Crucial for synchronous UI feedback)
APIs are text-based interfaces. You cannot simply "send a file" in a JSON body; you must serialize the binary data into a text string.
Goal: Convert the incoming binary stream into a Data URI (Base64)
We bypass the abstractions and use a generic HTTP Request node. This gives us full control over the payload structure.
Method: POST
URL: https://api.mistral.ai/v1/chat/completions
Headers:
• Authorization: Bearer YOUR_MISTRAL_API_KEY
• Content-Type: application/json
The Payload (JSON)
Here is where we specifically invoke pixtral-12b-2409. Note the dual content types (text for instructions, image_url for the vision data).
Note: The response_format: { "type": "json_object" } parameter is critical. Without it, the model may generate conversational text instead of returning pure data.
The API response arrives as a string nested inside a JSON object. We must parse it back into a JavaScript object for the frontend to consume.
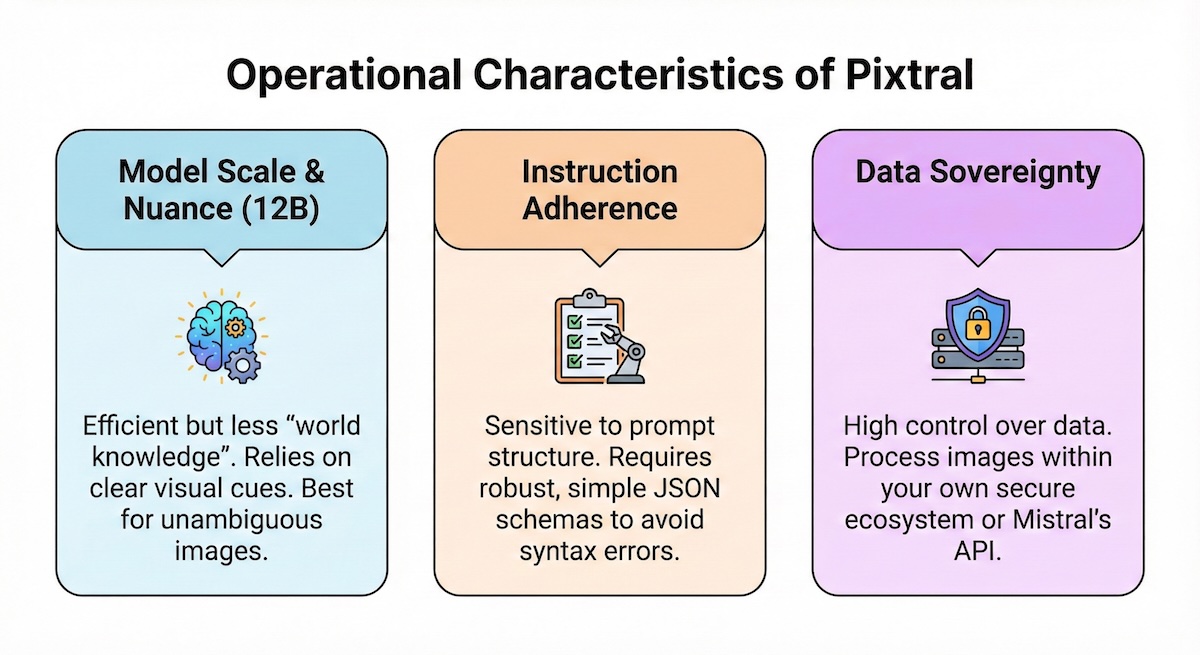
Operational Characteristics of Pixtral
When engineering with Pixtral-12b, you must account for its specific operational profile.
1. Model Scale & Nuance
Pixtral is a 12 Billion parameter model. While efficient, it operates with less "world knowledge" than significantly larger models. It relies heavily on clear visual cues and may struggle with highly ambiguous images where context is not visible.
2. Instruction Adherence
Smaller, efficient models are sensitive to prompt structure. Even with json_object mode enabled, Pixtral requires a robust and simple JSON schema. Complex, deeply nested schemas increase the probability of syntax errors in the output.
3. Data Sovereignty
Using Mistral's API or self-hosting the open weights allows for a high degree of data control. This architecture ensures that image data is processed within a specific ecosystem, which is a critical requirement for many internal tools.
Conclusion
Building with Mistral Pixtral requires a direct engineering approach—handling Base64 conversion and schema enforcement manually. This friction provides the benefit of granular control over the data pipeline and the ability to leverage a specialized multimodal model effectively.


